Navigating the Complexities of Consumer Rights in Brazil: A Comprehensive Guide to Consumer Protection
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Consumer Rights in Brazil: A Comprehensive Guide to Consumer Protection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Consumer Rights in Brazil: A Comprehensive Guide to Consumer Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of Consumer Rights in Brazil: A Comprehensive Guide to Consumer Protection

Brazil boasts a robust consumer protection framework, enshrined in the Consumer Protection Code (CDC). This legislation, enacted in 1990, provides a comprehensive set of rights and safeguards for consumers across the country. At its core, the CDC aims to establish a fair and balanced relationship between consumers and businesses, ensuring that consumers are treated with respect and have access to clear and accurate information about products and services.
One of the key pillars of the CDC is the right to complain and seek redress for any perceived injustice or violation of consumer rights. This right is exercised through a variety of mechanisms, including consumer protection agencies and consumer courts. These entities play a crucial role in mediating disputes between consumers and businesses, ensuring that consumers have a voice and can effectively advocate for their rights.
Understanding the Scope of Consumer Rights in Brazil
The CDC encompasses a wide range of consumer rights, encompassing various aspects of the consumer experience. These include:
- Right to Safety: Consumers have the right to purchase products and services that are safe and do not pose a risk to their health or well-being. This includes the right to be informed about potential risks associated with the product or service.
- Right to Information: Consumers have the right to receive clear, accurate, and complete information about products and services. This includes information about the product’s composition, features, price, warranty, and any potential risks associated with its use.
- Right to Choose: Consumers have the right to choose freely from a variety of products and services available in the market. This right is further strengthened by the prohibition of unfair competition and monopoly practices.
- Right to Fair Pricing: Consumers have the right to access products and services at fair prices, free from excessive markups or hidden charges. The CDC also prohibits price discrimination, ensuring that consumers are not charged different prices for the same product or service based on their personal characteristics.
- Right to Fair Contracts: Consumers have the right to clear and understandable contracts that outline their rights and obligations. Unfair or abusive clauses in contracts are deemed null and void under the CDC.
- Right to Repair and Replacement: Consumers have the right to have defective products repaired or replaced, depending on the nature of the defect and the product’s warranty. This right ensures that consumers are not left with faulty products and are provided with adequate solutions to rectify the situation.
- Right to Compensation: Consumers have the right to be compensated for any damages or losses incurred as a result of defective products or services, misleading advertising, or unfair business practices. This right ensures that consumers are made whole and are not unfairly burdened by the consequences of business misconduct.
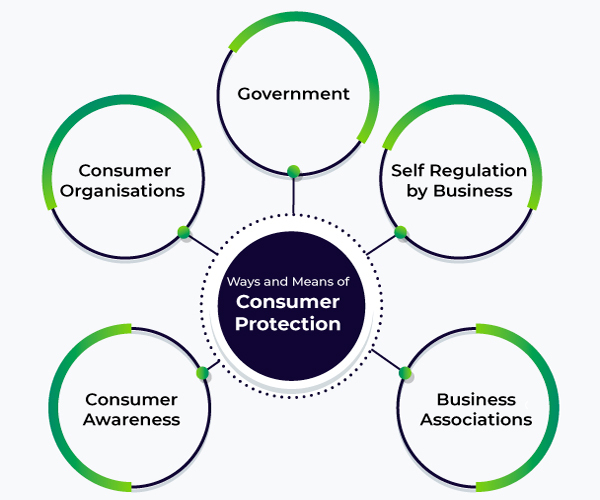
The Role of Consumer Protection Agencies
Consumer protection agencies, such as PROCON (Programa de Proteção e Defesa do Consumidor), play a crucial role in enforcing consumer rights in Brazil. These agencies are responsible for:
- Receiving and investigating consumer complaints: PROCON and other consumer protection agencies act as mediators between consumers and businesses, helping to resolve disputes amicably.
- Providing information and guidance to consumers: These agencies provide consumers with information about their rights and obligations, as well as guidance on how to file complaints and navigate the consumer protection system.
- Monitoring and enforcing consumer protection laws: PROCON and other agencies actively monitor the marketplace to identify and address violations of consumer protection laws. This includes conducting inspections of businesses and taking action against those engaging in unfair or illegal practices.
- Promoting consumer education and awareness: These agencies actively engage in public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about their rights and responsibilities, empowering them to become informed and assertive consumers.
Resolving Consumer Disputes: The Role of Consumer Courts
In cases where consumer disputes cannot be resolved through mediation or other alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, consumers have the right to seek redress in consumer courts. These specialized courts are designed to handle consumer-related disputes efficiently and effectively.
Consumer courts are empowered to:
- Review and adjudicate consumer complaints: These courts examine the evidence presented by both the consumer and the business, and determine whether the consumer’s rights have been violated.
- Issue rulings and impose sanctions: If the court finds that the consumer’s rights have been violated, it can issue a ruling in favor of the consumer and impose sanctions on the business, including fines, injunctions, and other remedies.
- Provide compensation to consumers: Consumer courts can order businesses to pay compensation to consumers for any damages or losses incurred as a result of the violation of their rights.
Navigating the Consumer Protection System: Practical Tips
Understanding your rights as a consumer and knowing how to effectively navigate the consumer protection system is essential for protecting your interests. Here are some practical tips to keep in mind:
- Be informed about your rights: Familiarize yourself with the provisions of the CDC and the specific rights it guarantees to consumers.
- Keep all documentation: Maintain records of all purchases, contracts, receipts, and any communication with businesses related to your purchase. This documentation will be crucial in case you need to file a complaint.
- Attempt to resolve disputes amicably: Before resorting to formal complaints or legal action, try to resolve the dispute directly with the business. Many companies have internal complaint resolution mechanisms that can be effective in resolving issues.
- File a formal complaint with PROCON or other consumer protection agencies: If your efforts to resolve the dispute amicably fail, file a formal complaint with the relevant consumer protection agency.
- Seek legal counsel if necessary: If your complaint is not resolved through mediation or other alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, you may need to seek legal advice from a qualified consumer protection lawyer.
FAQs: Addressing Common Consumer Concerns
Q: What are some common examples of consumer rights violations?
A: Some common examples include:
- Defective products: Products that malfunction, are unsafe, or do not meet the advertised specifications.
- Misleading advertising: Advertisements that make false or misleading claims about the product or service.
- Unfair contracts: Contracts that contain unfair or abusive clauses that are detrimental to the consumer.
- Price discrimination: Businesses charging different prices for the same product or service based on the consumer’s personal characteristics.
- Failure to provide adequate information: Businesses failing to provide consumers with clear and accurate information about the product or service.
Q: How can I file a complaint with PROCON?
A: You can file a complaint with PROCON online, by phone, or in person at a PROCON office. You will need to provide your personal information, details of the product or service, and a description of the issue.
Q: What are the consequences for businesses that violate consumer rights?
A: Businesses that violate consumer rights can face a range of consequences, including:
- Fines: PROCON and other consumer protection agencies can impose fines on businesses that violate consumer protection laws.
- Injunctions: Courts can order businesses to cease and desist from engaging in unfair or illegal practices.
- Compensation to consumers: Businesses can be ordered to pay compensation to consumers for any damages or losses incurred as a result of the violation of their rights.
- Publicity: PROCON and other agencies can publicize the names of businesses that violate consumer rights, damaging their reputation and goodwill.
Conclusion: Embracing a Culture of Consumer Protection
The CDC and the robust consumer protection framework in Brazil are critical for ensuring a fair and equitable marketplace for consumers. By understanding their rights and knowing how to effectively navigate the consumer protection system, consumers can protect themselves from unfair business practices and advocate for their interests. The ongoing efforts of consumer protection agencies and courts are crucial in empowering consumers and fostering a culture of respect and accountability within the Brazilian marketplace.

![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Consumer Rights in Brazil: A Comprehensive Guide to Consumer Protection. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!