Navigating the Trademark Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Trademark Classes
Related Articles: Navigating the Trademark Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Trademark Classes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Trademark Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Trademark Classes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Trademark Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Trademark Classes

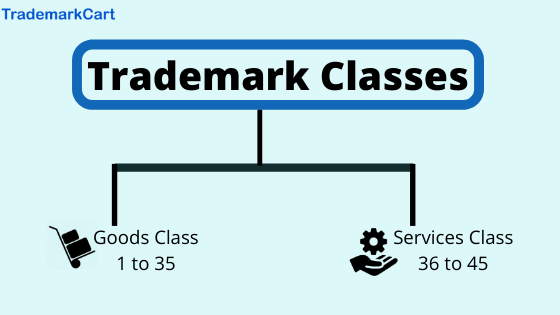
The world of trademarks, like any complex system, relies on a structured framework for organization and clarity. This framework is built upon the concept of trademark classes, a system that categorizes goods and services into distinct groups based on their nature and intended use. Understanding these classes is crucial for both trademark applicants and businesses seeking to protect their brand identity.
The International Classification of Goods and Services (Nice Agreement)
At the heart of this system lies the International Classification of Goods and Services (Nice Agreement), a globally recognized framework adopted by over 100 countries. This agreement establishes a standardized system for classifying goods and services into 45 distinct classes, with 34 classes dedicated to goods and 11 classes dedicated to services.
The Importance of Trademark Classes
The classification system serves several critical purposes:
- Clarity and Organization: By grouping similar goods and services, the system creates a logical and easily navigable framework for trademark registration and search. This facilitates efficient processing of applications and allows for comprehensive searches to identify potential conflicts.
- Protection Scope: Each trademark registration is limited to the specific goods or services designated in the application. The chosen class determines the scope of protection granted to the trademark, defining the range of products or services for which the trademark owner can assert exclusive rights.
- Global Recognition: The Nice Agreement fosters international harmonization, ensuring that trademark classifications are consistent across participating countries. This promotes cross-border trade and simplifies the process of protecting trademarks in multiple jurisdictions.
Exploring the Trademark Classes: A Comprehensive Overview
To understand the intricacies of trademark classes, let’s delve into a detailed examination of each category:
Class 1: Chemicals
This class encompasses a wide range of chemical products, including:
- Industrial chemicals: Acids, alkalis, salts, solvents, and other industrial chemicals.
- Agricultural chemicals: Fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides.
- Pharmaceutical chemicals: Medicines, vitamins, and other pharmaceutical products.
- Photographic chemicals: Developers, fixers, and other photographic chemicals.
Class 2: Paints, varnishes, lacquers, preservatives against rust and deterioration of wood
This class covers products used for coating, protecting, and enhancing surfaces:
- Paints: Acrylic, oil-based, water-based, and other types of paints.
- Varnishes: Clear coatings that protect and enhance wood, metal, and other surfaces.
- Lacquers: Thin, hard coatings that provide a protective and decorative finish.
- Preservatives: Products that prevent rust and deterioration of wood and other materials.
Class 3: Bleaching preparations and other substances for laundry use; cleaning, polishing, scouring and abrasive preparations; soaps; perfumery, essential oils, cosmetics, hair lotions; dentifrices.
This class includes products for personal hygiene, cleaning, and beautification:
- Laundry detergents: Powders, liquids, and other detergents used for washing clothes.
- Cleaning products: All-purpose cleaners, window cleaners, floor cleaners, and other cleaning agents.
- Soaps: Bar soaps, liquid soaps, and other soap-based products.
- Cosmetics: Makeup, skincare products, hair care products, and other beauty products.
- Perfumery: Fragrances, colognes, and other scented products.
Class 4: Lubricants, industrial oils and greases; fuels (including motor spirit) and illuminants; candles and wicks for lighting.
This class covers products used for lubrication, energy generation, and lighting:
- Lubricants: Oils, greases, and other products used to reduce friction between moving parts.
- Industrial oils: Oils used in manufacturing processes, such as cutting oils and hydraulic fluids.
- Fuels: Gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, and other fuels used for transportation and power generation.
- Candles: Wax candles, soy candles, and other types of candles used for illumination and decoration.
Class 5: Pharmaceuticals, medical and veterinary preparations; sanitary preparations for medical purposes; dietetic food and substances adapted for medical or veterinary use, food for babies; plasters, materials for dressings; absorbent articles for medical purposes; articles for the care of infants; disinfectants; preparations for destroying vermin; fungicides, herbicides.
This class encompasses products related to healthcare, hygiene, and medical treatment:
- Pharmaceuticals: Medicines, vitamins, and other pharmaceutical products.
- Medical devices: Bandages, bandages, and other medical devices.
- Sanitary preparations: Disinfectants, antiseptics, and other products used for hygiene.
- Dietary supplements: Vitamins, minerals, and other supplements used to enhance health.
- Veterinary products: Medicines, vaccines, and other products used to treat animals.
Class 6: Metal goods, not included in other classes; common metals and their alloys; metal building materials; transportable buildings of metal; materials of metal for railway tracks; non-electric cables and wires of common metal; ironmongery, small items of metal hardware; pipes and tubes of metal; safes; goods of common metal not included in other classes.
This class encompasses a wide range of metal products, including:
- Metal building materials: Steel beams, metal panels, and other materials used in construction.
- Metal hardware: Screws, nails, nuts, bolts, and other small metal hardware items.
- Metal pipes and tubes: Pipes and tubes used for plumbing, drainage, and other applications.
- Metal furniture: Tables, chairs, and other furniture made of metal.
- Metal containers: Cans, boxes, and other containers made of metal.
Class 7: Machines and machine tools; motors and engines (except for land vehicles); machine coupling and transmission components (except for land vehicles); agricultural implements other than hand-operated; incubators for eggs; machines for treatment of materials (except for land vehicles); machines for vending, money handling, and data processing; cash registers; calculating machines; data processing equipment; fire-extinguishing apparatus.
This class covers a broad range of machinery and equipment, including:
- Industrial machinery: Machines used in manufacturing, processing, and other industrial applications.
- Agricultural machinery: Tractors, combines, and other machines used in agriculture.
- Construction equipment: Excavators, bulldozers, and other machines used in construction.
- Office equipment: Printers, copiers, and other office machines.
- Data processing equipment: Computers, servers, and other data processing equipment.
Class 8: Hand tools and implements (hand-operated); cutlery; side arms; razors.
This class includes tools, implements, and weapons that are hand-operated:
- Hand tools: Hammers, screwdrivers, wrenches, and other tools used for manual work.
- Cutlery: Knives, forks, spoons, and other eating utensils.
- Side arms: Swords, daggers, and other weapons used for self-defense.
- Razors: Safety razors, straight razors, and other razors used for shaving.
Class 9: Scientific, nautical, surveying, photographic, cinematographic, optical, weighing, measuring, signalling, checking (supervision), life-saving and teaching apparatus and instruments; apparatus for recording, transmission or reproduction of sound or images; magnetic data carriers, recording discs; automatic vending machines and mechanisms for coin-operated apparatus; cash registers, calculating machines, data processing equipment, computers; fire-extinguishing apparatus.
This class encompasses a wide range of scientific, technical, and educational equipment and instruments:
- Scientific instruments: Microscopes, telescopes, and other instruments used for scientific research.
- Optical instruments: Cameras, binoculars, and other instruments used for viewing and recording images.
- Measuring instruments: Scales, rulers, and other instruments used for measuring length, weight, and other quantities.
- Data storage devices: Hard drives, flash drives, and other devices used for storing data.
- Computers: Personal computers, laptops, and other types of computers.
Class 10: Surgical, medical, dental and veterinary instruments and apparatus; artificial limbs, eyes and teeth; orthopedic articles; suture materials.
This class includes medical equipment and supplies used for healthcare and treatment:
- Surgical instruments: Scalpels, forceps, and other instruments used in surgery.
- Medical instruments: Stethoscopes, thermometers, and other instruments used for medical diagnosis and treatment.
- Dental instruments: Drills, probes, and other instruments used in dentistry.
- Veterinary instruments: Instruments used for treating animals.
- Artificial limbs: Prosthetics used to replace missing limbs.
Class 11: Apparatus and installations for lighting, heating, steam generating, cooking, refrigerating, drying, ventilating, water supply and sanitary purposes.
This class covers equipment and installations related to heating, cooling, and other essential services:
- Lighting fixtures: Lamps, chandeliers, and other lighting fixtures.
- Heating systems: Furnaces, boilers, and other heating systems.
- Refrigeration equipment: Refrigerators, freezers, and other refrigeration equipment.
- Water supply systems: Pumps, pipes, and other components used for water supply.
- Sanitary equipment: Toilets, sinks, and other sanitary fixtures.
Class 12: Vehicles; apparatus for locomotion by land, air or water.
This class encompasses a wide range of vehicles, including:
- Motor vehicles: Cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other motor vehicles.
- Aircraft: Planes, helicopters, and other aircraft.
- Watercraft: Boats, ships, and other watercraft.
- Railroad equipment: Trains, locomotives, and other railroad equipment.
Class 13: Firearms; ammunition and projectiles; explosives; fireworks.
This class covers weapons, ammunition, and explosives:
- Firearms: Guns, rifles, pistols, and other firearms.
- Ammunition: Bullets, shells, and other ammunition used in firearms.
- Explosives: Dynamite, gunpowder, and other explosives.
- Fireworks: Fireworks used for entertainment and celebrations.
Class 14: Jewelry, precious metals and their alloys and goods in precious metals or coated therewith; horological and chronometric instruments.
This class includes precious metals, jewelry, and timepieces:
- Jewelry: Rings, necklaces, earrings, and other jewelry made of precious metals.
- Precious metals: Gold, silver, platinum, and other precious metals.
- Timepieces: Watches, clocks, and other timekeeping devices.
- Horological instruments: Instruments used for measuring time.
Class 15: Musical instruments.
This class covers instruments used for creating music:
- String instruments: Guitars, violins, cellos, and other string instruments.
- Wind instruments: Flutes, clarinets, trumpets, and other wind instruments.
- Keyboard instruments: Pianos, organs, and other keyboard instruments.
- Percussion instruments: Drums, cymbals, and other percussion instruments.
Class 16: Paper, cardboard and goods made from these materials, not included in other classes; printed matter; bookbinding material; photographs; stationery; adhesives for stationery or household purposes; artists’ materials; paint brushes; typewriters and office requisites (except furniture); instructional and teaching materials (except apparatus); plastic materials for packaging; playing cards; printers’ type; printing blocks.
This class encompasses a wide range of paper products, stationery, and printing materials:
- Paper products: Paper, cardboard, envelopes, and other paper products.
- Stationery: Pens, pencils, notebooks, and other stationery items.
- Printing materials: Ink, toner, and other printing materials.
- Artists’ materials: Paints, brushes, and other art supplies.
- Packaging materials: Plastic bags, boxes, and other packaging materials.
Class 17: Rubber, gutta-percha, gum, asbestos, mica and goods made from these materials not included in other classes; plastics in extruded form for use in manufacture; packing, stopping and insulating materials; flexible pipes not of metal.
This class covers various materials and products made from rubber, plastics, and other similar materials:
- Rubber products: Tires, hoses, and other rubber products.
- Plastic products: Plastic bags, bottles, and other plastic products.
- Packing materials: Foam, cork, and other materials used for packing and insulation.
- Flexible pipes: Pipes made of rubber, plastic, or other flexible materials.
Class 18: Leather and imitations of leather; animal skins and hides; trunks and travelling bags; umbrellas, parasols and walking sticks; whips, harness and saddlery.
This class includes leather goods, luggage, and related items:
- Leather products: Leather jackets, belts, and other leather goods.
- Luggage: Suitcases, briefcases, and other travel bags.
- Umbrellas and parasols: Umbrellas, parasols, and walking sticks.
- Harness and saddlery: Saddles, bridles, and other equestrian equipment.
Class 19: Building materials (non-metallic); non-metallic rigid pipes for building; asphalt, pitch and bitumen; non-metallic transportable buildings; monuments, not of metal.
This class covers non-metallic building materials, including:
- Building materials: Bricks, concrete, and other non-metallic building materials.
- Pipes: Pipes made of plastic, ceramic, or other non-metallic materials.
- Asphalt and bitumen: Materials used for paving and roofing.
- Non-metallic buildings: Buildings made of wood, concrete, or other non-metallic materials.
Class 20: Furniture, mirrors, picture frames; articles made of wood, cork, reed, cane, wicker, horn, bone, ivory, whalebone, shell, amber, mother-of-pearl, meerschaum and substitutes for all these materials, not included in other classes; goods of these materials or substitutes for these materials, not included in other classes.
This class encompasses furniture, decorative items, and other products made from various natural and synthetic materials:
- Furniture: Tables, chairs, beds, and other furniture items.
- Mirrors: Mirrors used for reflection and decoration.
- Picture frames: Frames used for displaying pictures and artwork.
- Wooden products: Wooden toys, wooden furniture, and other wooden products.
- Cork products: Cork stoppers, cork flooring, and other cork products.
Class 21: Household or kitchen utensils and containers; combs and sponges; brushes (except paint brushes); brush-making materials; articles for cleaning purposes; steel wool; unworked or semi-worked glass (except glass used in building); glassware, porcelain and earthenware.
This class covers household goods, kitchenware, and tableware:
- Kitchen utensils: Pots, pans, knives, and other kitchen utensils.
- Tableware: Plates, cups, and other tableware items.
- Cleaning supplies: Cleaning brushes, sponges, and other cleaning supplies.
- Glassware: Glass bottles, jars, and other glassware items.
- Porcelain and earthenware: Porcelain and earthenware dishes, cups, and other tableware items.
Class 22: Ropes and cables, not of metal; nets; awnings and tents; sails; tarpaulins; sacks; bags (not included in other classes); padding and stuffing materials (except of rubber or plastics); raw fibrous textile materials.
This class encompasses ropes, cables, textiles, and related products:
- Ropes and cables: Ropes and cables made of natural or synthetic fibers.
- Nets: Fishing nets, safety nets, and other types of nets.
- Tents and awnings: Tents, awnings, and other outdoor structures.
- Bags and sacks: Bags and sacks used for storage and transportation.
- Textile fibers: Cotton, wool, and other raw textile fibers.
Class 23: Yarns and threads; textile goods, not included in other classes; bed covers; table covers.
This class covers textile goods, including yarns, fabrics, and household textiles:
- Yarns and threads: Cotton yarn, wool yarn, and other types of yarn.
- Textile fabrics: Cotton fabrics, silk fabrics, and other types of fabric.
- Bed covers: Blankets, sheets, and other bed covers.
- Table covers: Tablecloths, napkins, and other table covers.
Class 24: Textiles and textile goods, not included in other classes; carpets, rugs, mats and matting; linoleum and other materials for covering floors; wall hangings (non-textile).
This class encompasses a range of textile and flooring products:
- Textiles: Fabrics, yarns, and other textile materials.
- Carpets and rugs: Carpets, rugs, and mats used for flooring.
- Flooring materials: Linoleum, vinyl flooring, and other flooring materials.
- Wall hangings: Wall coverings, wallpaper, and other wall decorations.
Class 25: Clothing, footwear, headwear.
This class includes clothing, footwear, and headwear:
- Clothing: Shirts, pants, dresses, and other clothing items.
- Footwear: Shoes, boots, sandals, and other footwear items.
- Headwear: Hats, caps, and other headwear items.
Class 26: Lace, ribbons, embroidery and other trimmings; buttons, hooks and eyes; artificial flowers; hair ornaments.
This class covers decorative and ornamental items used for clothing and other purposes:
- Lace and ribbons: Lace, ribbons, and other decorative trimmings.
- Buttons and hooks: Buttons, hooks, and eyes used for fastening clothing.
- Artificial flowers: Artificial flowers used for decoration.
- Hair ornaments: Hair clips, barrettes, and other hair ornaments.
Class 27: Carpets, rugs, mats and matting; linoleum and other materials for covering floors; wall hangings (non-textile).
This class covers a range of textile and flooring products:
- Textiles: Fabrics, yarns, and other textile materials.
- Carpets and rugs: Carpets, rugs, and mats used for flooring.
- Flooring materials: Linoleum, vinyl flooring, and other flooring materials.
- Wall hangings: Wall coverings, wallpaper, and other wall decorations.
Class 28: Games and playthings; gymnastic and sporting articles; decorations for Christmas trees.
This class includes toys, games, and sporting goods:
- Toys: Dolls, toy cars, and other toys for children.
- Games: Board games, card games, and other games.
- Sporting goods: Balls, bats, rackets, and other sporting equipment.
- Christmas decorations: Decorations used for Christmas trees and other holiday celebrations.
**Class 29: Meat, fish, poultry and game; meat extracts; preserved







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Trademark Landscape: Understanding the Significance of Trademark Classes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!